Intermediate SQL and Basic CASE statements
You'll learn how to build categorical variables, aggregate data into a single column with numerous filtering criteria, and calculate counts and percentages using the CASE WHEN statement.

You’ll learn how to build categorical variables, aggregate data into a single column with numerous filtering criteria, and calculate counts and percentages using the CASE WHEN statement.
Basic CASE statements
Select the title and the ID from the wp_posts table:
SELECT
-- Select the title and the ID
post_title,
ID
FROM wp_posts
-- Only include these IDs
WHERE ID IN (21, 35);Count the number of meta keys the posts have from the wp_postmeta table. The result will be three items.
-- Count the meta kyes each post has
SELECT
CASE WHEN post_id = 2322 THEN 'Basic CASE statements'
WHEN post_id = 2280 THEN 'Introduction to Git'
ELSE 'Other' END AS title,
COUNT(post_id) AS total_matches
FROM wp_postmeta
-- Group by the CASE statement alias
GROUP BY title;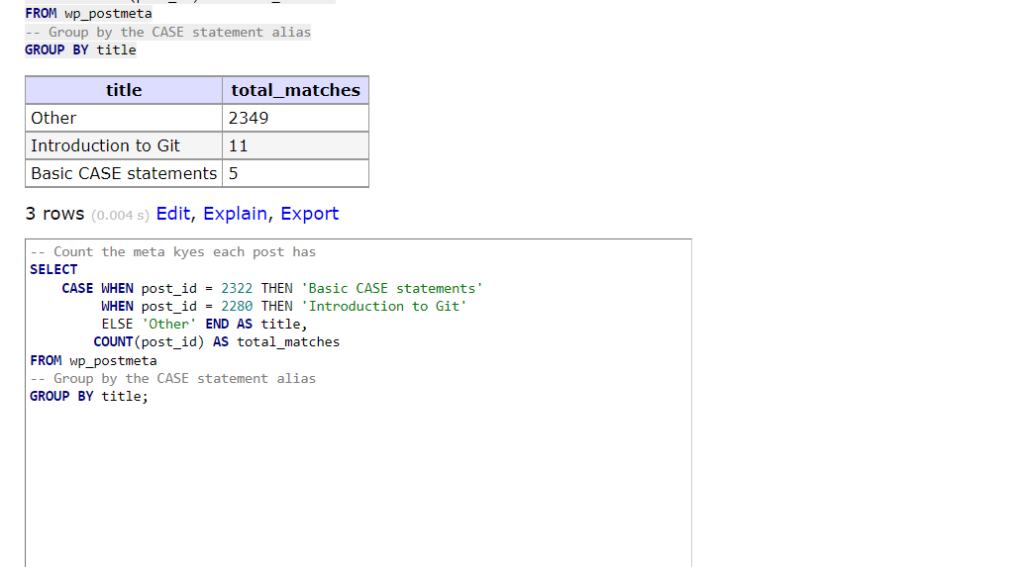
CASE statements comparing column values
Select the dates when a user visited the site before and after a certain date.
SELECT
-- Select the time when the user visited the site
viewed,
CASE WHEN viewed > '2022-03-26 23:29:53' THEN 'After 26 of March'
WHEN viewed < '2022-03-26 23:29:53' THEN 'Before 26 of March'
ELSE 'March 26' END AS visit
FROM wp_user_activity_info ORDER BY viewed DESC;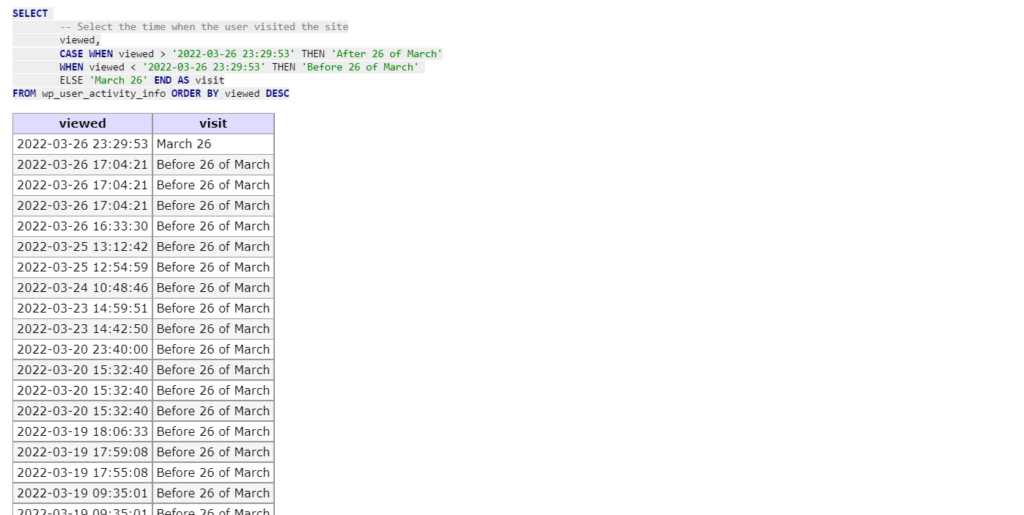
You can join more tables. The result will be an array of two columns. The first one will show the country code, and the second one will show if that user visited before a certain date or not.
SELECT
m.country_code,
-- Complete the CASE statement with an alias
CASE WHEN viewed > '2022-03-26 23:29:53' THEN 'After 26 of March'
WHEN viewed < '2022-03-26 23:29:53' THEN 'Before 26 of March'
ELSE 'March 26' END AS visit
FROM wp_user_activity AS m
LEFT JOIN wp_user_activity_info AS t
ON m.ID = t.activity_id ORDER BY m.country_code ASCLimit the search by column. The result will be three columns. Country code, post, and when the post was viewed.
SELECT
m.country_code, t.post,
-- Complete the CASE statement with an alias
CASE WHEN viewed > '2022-03-26 23:29:53' THEN 'After 26 of March'
WHEN viewed < '2022-03-26 23:29:53' THEN 'Before 26 of March'
ELSE 'March 26' END AS visit
FROM wp_user_activity AS m
LEFT JOIN wp_user_activity_info AS t
ON m.ID = t.activity_id WHERE t.taxonomy= 'post_tag' ORDER BY m.country_code ASC;It’s important to analyze which rows of your data are part of your ELSE clause and if they’re appropriately categorized when evaluating logical conditions.
You may use AND within your WHEN clause to test several logical criteria in a CASE statement.
Was this post helpful? ( Answers: 1 )
Leave a comment
If you enjoyed this post or have any questions, please leave a comment below. Your feedback is valuable!